how to analyze uv absorptions from graph|uv visible spectrophotometer diagram : white label This page takes a brief look at how UV-visible absorption spectra can be used to help identify compounds and to measure the concentrations of colored solutions. It assumes . bbw copacabana butt - read the comments pictures and videos on EroMe. The album about bbw copacabana butt - read the comments is to be seen for free on EroMe .
{plog:ftitle_list}
- Lojas Bibelô - Lojas Bibelô
Looking at UV-vis spectra. We have been talking in general terms about how molecules absorb UV and visible light – now let’s look at some actual examples of data from a UV-vis absorbance spectrophotometer.
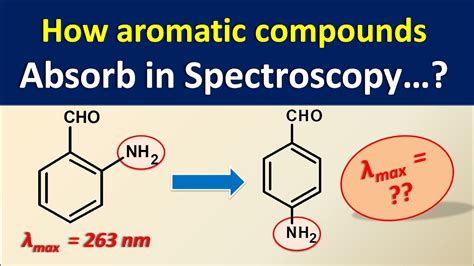
The diagram below shows a simple UV-visible absorption spectrum for buta-1,3-diene - a molecule we will talk more about later. Absorbance (on the vertical axis) is just a measure of the amount of light absorbed. This page takes a brief look at how UV-visible absorption spectra can be used to help identify compounds and to measure the concentrations of colored solutions. It assumes .
We have been talking in general terms about how molecules absorb UV and visible light – now let's look at some actual examples of data from a UV-vis absorbance .
Quartz cuvettes are designed for use in UV-visible spectrophotometry. When handling the cuvette, avoid touching the sides the light will pass through (generally, the clear sides of . Choose and set the . Using UV-absorption spectra to help identify organic compounds. If you have worked through the rest of this section, you will know that the wavelength of maximum absorption (lambda-max) depends on the presence of particular chromophores (light-absorbing groups) in a molecule. . Then you plot a graph of that absorbance against concentration . How To Interpret IR Spectra In 1 Minute Or Less: The 2 Most Important Things To Look For [Tongue and Sword] Last post, we briefly introduced the concept of bond vibrations, and we saw that we can think of .
UV-Vis spectroscopy analysis, absorption spectrum and absorbance units. UV-Vis spectroscopy information may be presented as a graph of absorbance, optical density or transmittance as a function of wavelength. However, the information is more often presented as a graph of absorbance on the vertical y axis and wavelength on the horizontal x axis .The region from 4000 to 2500 cm –1 corresponds to absorptions caused by N–H, C–H, and O–H single-bond stretching motions. N–H and O–H bonds absorb in the 3300 to 3600 cm –1 range; C–H bond stretching occurs near 3000 cm –1.; The region from 2500 to 2000 cm –1 is where triple-bond stretching occurs. Both C≡N C≡N and C≡C C≡C bonds absorb here. Overall, the graph shows how different ETL materials in different concentrations emit light, and it is often used as a parameter for measuring how effective the material is as the electron transport layer. Figure 3(c) shows the radioactive decay of the excited state. The photoluminescence intensity is decreasing over 50 ns.
The spectra were recorded using a UV–vis–NIR spectrophotometer (UV-3600 Shimadzu) equipped with a 15 cm integrating sphere in the spectral range 250–800 nm. Each time the sample holder was rotated to a different position (by ∼45°). Barium sulfate (BaSO 4, Riedel-de Haen) was used to dilute the samples (1:100) and was used as a reference.If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Understand the Beer-Lambert law for absorbance, A = ɛ x l x c. The standard equation for absorbance is A = ɛ x l x c, where A is the amount of light absorbed by the sample for a given wavelength, ɛ is the molar absorptivity, l is the distance that the light travels through the solution, and c is the concentration of the absorbing species per unit volume. . Click here to see more posts about UV-Vis. If the isoprene spectrum on the right was obtained from a dilute hexane solution (c = 4 * 10-5 moles per liter) in a 1 cm sample cuvette, a simple calculation using the above formula indicates a molar absorptivity of 20,000 at the maximum absorption wavelength. Indeed the entire vertical absorbance scale may be .
Click here to see more posts about UV-Vis. If the isoprene spectrum on the right was obtained from a dilute hexane solution (c = 4 * 10-5 moles per liter) in a 1 cm sample cuvette, a simple calculation using the above formula indicates a molar absorptivity of 20,000 at the maximum absorption wavelength. Indeed the entire vertical absorbance scale may be . If the species you are measuring is one that has been commonly studied, literature reports or standard analysis methods will provide the \(\lambda\) max value. If it is a new species with an unknown \(\lambda\) max value, then it is easily .
what compounds absorb uv light
Dye Concentration Using UV-Vis v5 2 • Molar absorptivity – a measure of how strongly a sample absorbs light at a given wavelength; it is a physical property of a compound • Organic molecule – a molecule that contains carbon • Solute – the component in lesser amount in a solution • Solvent – the major component of a solution Plots of the predicted UV/Visible spectrum for a molecule use this numeric data from each of the computed excited states. Conventionally, UV-Visible spectra area plotted as ε vs. λ (excitation wavelength in nm), and the peaks assume a Gaussian band shape. The equation of a Gaussian band shape is: [Equation 1]Based on the UV-Vis spectrum that you are attaching in your question, much analysis can be done: 1. The type of transition that correspond to the peak that is showed in the spectrum.Where A is absorbance, c is the molar concentration of the molecule in solution, and l is the path length through the sample (often the width of the cuvette, or the total film). You can use this calculation to measure the concentration of a .
refractometer conversion tool
Wide Range of Application: Infrared spectroscopy could be used to analyze almost all organic compounds and some inorganic compounds. It has a wide range of application in both qualitative analysis and quantitative .analysis of UV-VIS spectral data in terms of determining the structure of chemical compounds. Therefore, this paper contains guidelines that are used as information on how to read and interpret data from the UV-VIS spectrum in terms of determining the structure of chemical compounds. Steps on how to analyze the UV-VIS spectrum are presented.
Notice also that the convention in UV-vis spectroscopy is to show the baseline at the bottom of the graph with the peaks pointing up. Wavelength values on the x-axis are generally measured in nanometers (nm). Peaks in UV spectra tend to be quite broad, often spanning well over 20 nm at half-maximal height.
refractometer conversion wine
uv visible spectroscopy diagram
%PDF-1.6 %âãÏÓ 600 0 obj > endobj 624 0 obj >/Filter/FlateDecode/ID[0D68C31A8E0937438E797621B9C54FBD>81B828330A4A3B4A91845ACEAE23EA1A>]/Index[600 45]/Info 599 0 R . UV/Vis spectrum for the metal–ligand complex \(\text{Fe(phen)}_3^{2+}\), where phen is the ligand o-phenanthroline. Comparing the IR spectrum in Figure 10.2.2 to the UV/Vis spectrum in Figure 10.2.4 shows us that UV/Vis absorption bands are often significantly broader than those for IR absorption. Looking at the graph that measures absorbance and wavelength, an isosbestic point can also be observed. An isosbestic point is the wavelength in which the absorbance of two or more species are the same. The appearance of an isosbestic point in a reaction demonstrates that an intermediate is NOT required to form a product from a reactant.

UV-Vis spectroscopy is used to quantify the amount of DNA or protein in a sample, for water analysis, and as a detector for many types of chromatography. Kinetics of chemical reactions are also measured with UV-Vis spectroscopy by taking repeated UV-Vis measurements over time. UV-Vis measurements are generally taken with a spectrophotometer.
Beer's Law. There are three factors that influence the number of photons absorbed as light travels through a sample (figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Path length (the longer the path length the greater the number photons absorbed).; Concentration of absorbing molecules (typically solute molecules, the more concentrated the more photons absorbed); Intensity of the light .Beckman DU640 UV/Vis spectrophotometer. Ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy or ultraviolet–visible (UV–VIS) spectrophotometry [1] [2] [3] refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. [2] Being relatively inexpensive and easily implemented, this methodology is widely .analysis of UV-VIS spectral data in terms of determining the structure of chemical compounds. Therefore, this paper contains guidelines that are used as information on how to read and interpret data from the UV-VIS spectrum in terms of determining the structure of chemical compounds. Steps on how to analyze the UV-VIS spectrum are presented.
How to Read FTIR Analysis Results Graphs The X-Axis: The Infrared Spectrum. The x-axis—or horizontal axis—represents the infrared spectrum, which plots the intensity of infrared spectra. The peaks, which are also called absorbance bands, correspond with the various vibrations of the sample’s atoms when it’s exposed to the infrared .
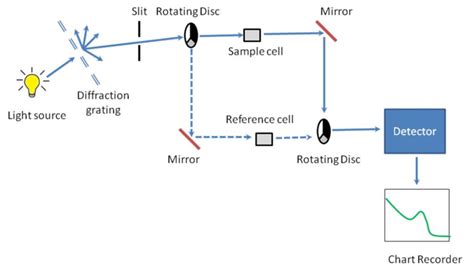
uv visible spectrophotometer diagram
If you’re a soccer fan who always wanted to know the live stat.
how to analyze uv absorptions from graph|uv visible spectrophotometer diagram